A collection of clinical insights from our team of in-house pharmacists. These industry veterans curate, update and review our patented technology’s 34,000+ clinical, dose-adjusted savings suggestions—and they’ve got expertise to share.
Check back for more condition-focused content, featuring key trends we’re seeing in utilization, medical management, pricing, therapeutic alternatives and more.
———————————————–
This month, in recognition of Thyroid Awareness Month we turn our attention to hypothyroidism. This is the most common form of thyroid disorders and effects about 5% of the population, with a further 5% estimated as undiagnosed.
Condition Summary
- The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland in the middle of the neck that produces two types of thyroid hormones commonly referred to as T3 and T4. These hormones control your body’s metabolism.
- Hypothyroidism (or an underactive thyroid) is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce as much thyroid hormone as it normally should.
- Symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary widely and often imitate signs of normal aging, which is why so many people go undiagnosed. Most people complain of lack of energy, increased sensitivity to cold temperatures, thinning hair, dry skin or constipation.
- If not treated, hypothyroidism can affect the heart and lungs, as well as hinder women’s ability to get pregnant.
Treatment
- Hypothyroidism can be detected by a simple blood test that measures thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) levels.
- While there is no cure, most cases can be completely controlled by replacement therapy that restores hormone levels to normal. Hormone levels are then typically measured every six weeks to determine the correct replacement dosage.
- Replacement therapy is usually prescribed in an oral form of T4 (levothyroxine), which is available in a tablet, soft gel capsule and liquid formulations. The brand-name and generic versions are typically color-coded the same and available in multiple strengths to allow for precise dosing.
- Notable controversy about differences between brand-name and generic formulations were resolved in 1997. Today, these different formulations are considered equally effective and taken once per day—typically in the morning—on an empty stomach.
- Some clinicians may also prescribe the other thyroid hormone, T3, in combination with T4. However, since T4 is converted into T3 in every human organ, most studies have shown no advantage to combining T3 and T4 therapy, compared to taking T4 alone.
Utilization Snapshot
Rx Savings Solutions members are prescribed over 130 different thyroid replacement products or strengths—and spent more than $57 million in 2021 to treat hypothyroidism. While the industry averages for claims are around $20 per fill, newer capsule and liquid formulations can cost over $300 for a 90-day supply.
Key Trend
Levothyroxine Sodium 50mcg Tablet is the most common form and strength used today. However, the branded version, Synthroid®, still has significant utilization because of the previous concerns about generic efficacy we mentioned above. That said, we are expecting to see Synthroid usage drop as the drug is removed from some national formularies starting in 2022. Here’s a look at the cost differences we’re seeing in the market today using industry averages:
- Levothyroxine 50mcg Tablet = $14/#90
- Synthroid 50mcg Tablet = $81/#90
- Tirosint 50mcg Capsule = $340/#90
Potential Member Savings
While we’re expecting some brand-to-generic utilization changes in 2022, our RxSS software finds savings opportunities like this all the time. It’s the same treatment, but by simply changing from a capsule to a tablet—called a dose formulation change—we may be able to help a member and their health plan save around $1,250 a year.
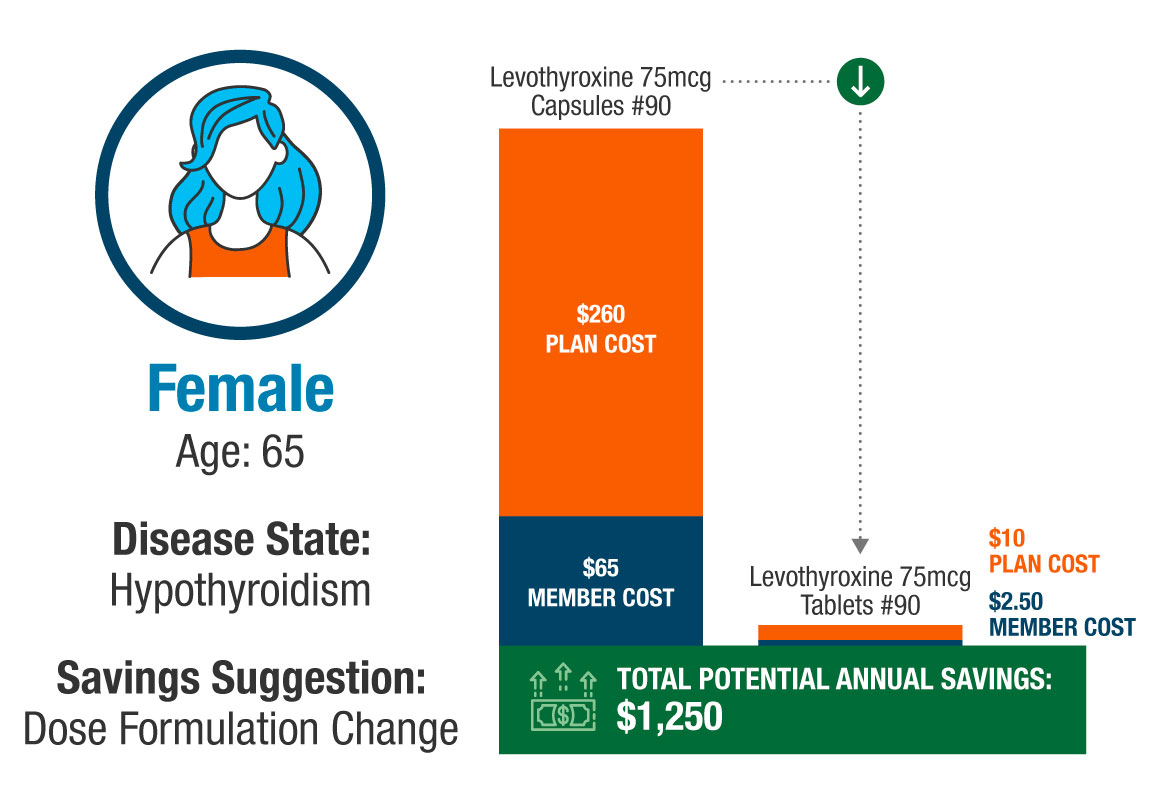
* prices shown reflect industry averages
———————————————–
Meet Our Pharmacists
How can RxSS find so many ways to save on prescriptions? First, we find smart pharmacists. Learn all about our Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee and what they do.

